Mô tả
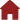
Tungsten carbide (chemical formula: WC) is a chemical compound (specifically, a carbide) containing equal parts of tungsten and carbon atoms. In its most basic form, tungsten carbide is a fine gray powder, but it can be pressed and formed into shapes through a process called sintering for use in industrial machinery, cutting tools, abrasives, armor-piercing shells and jewellery.
Tungsten carbide is approximately twice as stiff as steel, with a Young’s modulus of approximately 530–700 GPa (77,000 to 102,000 ksi),[4][7][8][9] and is double the density of steel—nearly midway between that of lead and gold. It is comparable with corundum (α-Al2O3) in hardness and can be polished and finished only with abrasives of superior hardness such as cubic boron nitride and diamond powder, wheels and compounds.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Tungsten carbide | |
| Other names Tungsten(IV) carbide Tungsten tetracarbide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.918 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UN number | 3178 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Properties | |
| WC | |
| Molar mass | 195.85 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Grey-black lustrous solid |
| Density | 15.63 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 2,785–2,830 °C (5,045–5,126 °F; 3,058–3,103 K)[3][2] |
| Boiling point | 6,000 °C (10,830 °F; 6,270 K) at 760 mmHg[2] |
| Insoluble | |
| Solubility | Soluble in HNO 3, HF[3] |
| 1·10−5 cm3/mol[3] | |
| Thermal conductivity | 110 W/(m·K)[4] |
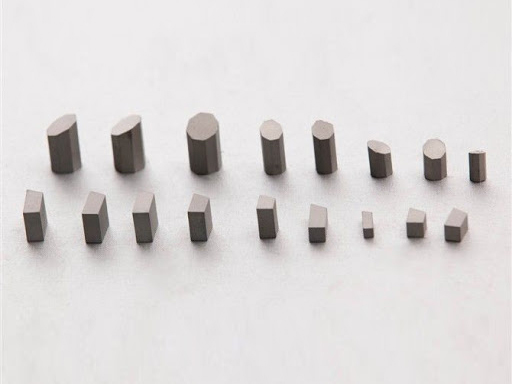
| Structure | |
| Hexagonal, hP2[5] | |
| P6m2, No. 187[5] | |
| 6m2[5] | |
a = 2.906 Å, c = 2.837 Å[5] α = 90°, β = 90°, γ = 120° | |
| Trigonal prismatic (center at C)[6] | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C) | 39.8 J/(mol·K)[4] |
Std molar entropy (S | 32.1 J/mol·K |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions | Tungsten boride Tungsten nitride |
Other cations | Molybdenum carbide Titanium carbide Silicon carbide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |